Introduction to Health & Healthcare in India
Why health is important cannot be overstated in today’s fast-paced world. Your physical and mental wellbeing determines your quality of life, productivity, and happiness. The ancient saying “health is wealth” holds more truth now than ever before, as medical emergencies can devastate family finances within hours.
India’s healthcare landscape is undergoing dramatic transformation. With rising lifestyle diseases, pollution, and stress-related conditions, healthcare costs have skyrocketed by 14% annually over the past five years. A single hospitalization for conditions like dengue, heart attack, or COVID-19 can cost anywhere from ₹50,000 to ₹5 lakhs or more.
Why health insurance is important becomes crystal clear when you consider these statistics: Over 55 million Indians fall into poverty each year due to medical expenses. The middle class is particularly vulnerable, as they earn too much to qualify for government schemes but struggle to afford quality private healthcare.
Healthcare in India presents a paradox. We have world-class hospitals and doctors in metros, yet rural areas lack basic medical facilities. Private healthcare delivers excellent service but at premium prices, while government hospitals are overburdened. This gap makes health insurance not just beneficial but essential for every Indian family.
Your lifestyle choices, environmental factors, and daily habits directly impact your health outcomes. Sedentary work, processed foods, air pollution, and inadequate sleep are creating a health crisis among young Indians. Prevention through healthy living combined with financial protection through insurance creates a robust health security framework.
What is Health Insurance?
How health insurance works is simpler than most people think. Health insurance is a contract where you pay a yearly fee (premium) to an insurance company, and in return, they cover your medical expenses when you fall sick or need hospitalization.
Think of it as a safety net. You pay small amounts regularly, and the insurer pays large hospital bills when needed. This protects your savings from being wiped out by unexpected medical emergencies.
Key Terms You Must Know:
Premium: The amount you pay yearly to keep your policy active. This typically ranges from ₹5,000 to ₹30,000+ depending on coverage.
Sum Insured: The maximum amount the insurer will pay for your medical expenses in one year. Common amounts are ₹5 lakh, ₹10 lakh, or ₹25 lakh.
Network Hospitals: Hospitals tied up with your insurer where you can get cashless treatment without paying upfront.
Deductible: The amount you pay from your pocket before insurance kicks in. Higher deductibles mean lower premiums.
Co-payment: A percentage of the bill you must pay yourself, typically 10-20% for senior citizens.
How Health Insurance Works in India:
Let’s understand with a real example. Rajesh has a health insurance policy with ₹5 lakh sum insured. He suffers a heart attack and gets admitted to a network hospital. The total bill comes to ₹3.5 lakhs. Here’s what happens:
- Hospital verifies Rajesh’s policy with the insurer
- Insurance company approves cashless treatment
- Rajesh gets treatment worth ₹3.5 lakhs
- Hospital bills the insurance company directly
- Rajesh pays nothing (except perhaps room rent difference if he chose a higher category room)
If Rajesh had gone to a non-network hospital, he would pay the bill first and then submit documents to get reimbursed by the insurer within 15-30 days.
What health insurance covers includes hospitalization for over 24 hours, day-care procedures (surgeries that don’t need overnight stay like cataract, dialysis), pre and post-hospitalization expenses (typically 30-60 days before and after), ambulance charges, and room rent up to specified limits.
Health Insurance Industry in India (2025 Overview)

When health insurance started in India dates back to 1912 with the Insurance Act, but modern health insurance emerged in 1986 when Mediclaim was launched by public sector insurers. The real revolution began in 2000 when private companies entered the market after insurance sector liberalization.
Fast forward to 2025, and India’s health insurance industry has become a ₹1 lakh crore market. Over 50 crore Indians now have some form of health coverage, though this is still less than 40% of the population. The gap between insured and uninsured remains a concern for policymakers.
How health insurance companies make money follows a straightforward model. They collect premiums from millions of policyholders, and since not everyone files claims in the same year, the company keeps the difference. They also invest premium money in government securities and bonds, earning returns. The key is maintaining a healthy “claims ratio” – ideally paying out 70-85% of premiums as claims while keeping 15-30% for operations and profit.
2025 Healthcare Trends:
Digital health insurance has exploded. You can now buy policies in 10 minutes online, file claims via apps, and get instant approvals. Telemedicine is covered by most insurers, and AI-powered health assessments are becoming standard.
IRDAI rules 2025 have brought consumer-friendly changes. Insurers must now settle cashless claims within 1 hour for emergencies. Pre-existing disease waiting periods have been reduced from 4 years to 3 years for most conditions. Mental health coverage is now mandatory in all comprehensive plans.
Why premiums are increasing in India concerns every policyholder. Medical inflation runs at 10-14% annually – much higher than general inflation. Advanced treatments, imported medical devices, and higher hospitalization rates push costs up. Natural calamities and pandemics have increased claim frequencies. In 2024-25 alone, most insurers hiked premiums by 15-25%, the steepest increase in a decade.
Types of Health Insurance in India
Choosing the right policy type is crucial for adequate protection. Let’s explore your options:
Individual Health Insurance
Covers one person with a dedicated sum insured. Best for single professionals or when family members need different coverage levels. Premium starts around ₹5,000-₹8,000 annually for a 30-year-old with ₹5 lakh coverage.
Family Floater Health Insurance
Which health insurance is best for families? Family floater plans cover your entire family (spouse, children, sometimes parents) under one policy with a shared sum insured. If your sum insured is ₹10 lakhs, any family member can use any amount up to this limit. It’s cost-effective compared to buying individual policies for everyone.
For a family of four (two adults, two children), a ₹10 lakh floater costs ₹15,000-₹20,000 annually – almost 40% cheaper than individual plans.
Senior Citizen Health Insurance
Specialized plans for people above 60 years. These policies accommodate pre-existing conditions, offer higher sum insured options, and include features like daily hospital cash and health check-ups. Premium is higher due to increased health risks – expect ₹25,000-₹50,000+ annually for ₹5 lakh coverage.
Top-Up Health Insurance Plans
These are smart add-ons that provide extra coverage once your base policy limit is exhausted. A top-up of ₹10 lakhs costs only ₹3,000-₹5,000 annually compared to ₹15,000+ for a standalone ₹10 lakh policy. The catch is you must first exhaust your deductible (base cover) before the top-up activates.
Corporate and Government Health Insurance
Employer-provided coverage or government schemes like Ayushman Bharat. While valuable, these are often insufficient. Corporate policies typically offer ₹3-5 lakhs coverage, which is inadequate for serious illnesses. Smart individuals supplement with personal policies.
What Health Insurance Covers
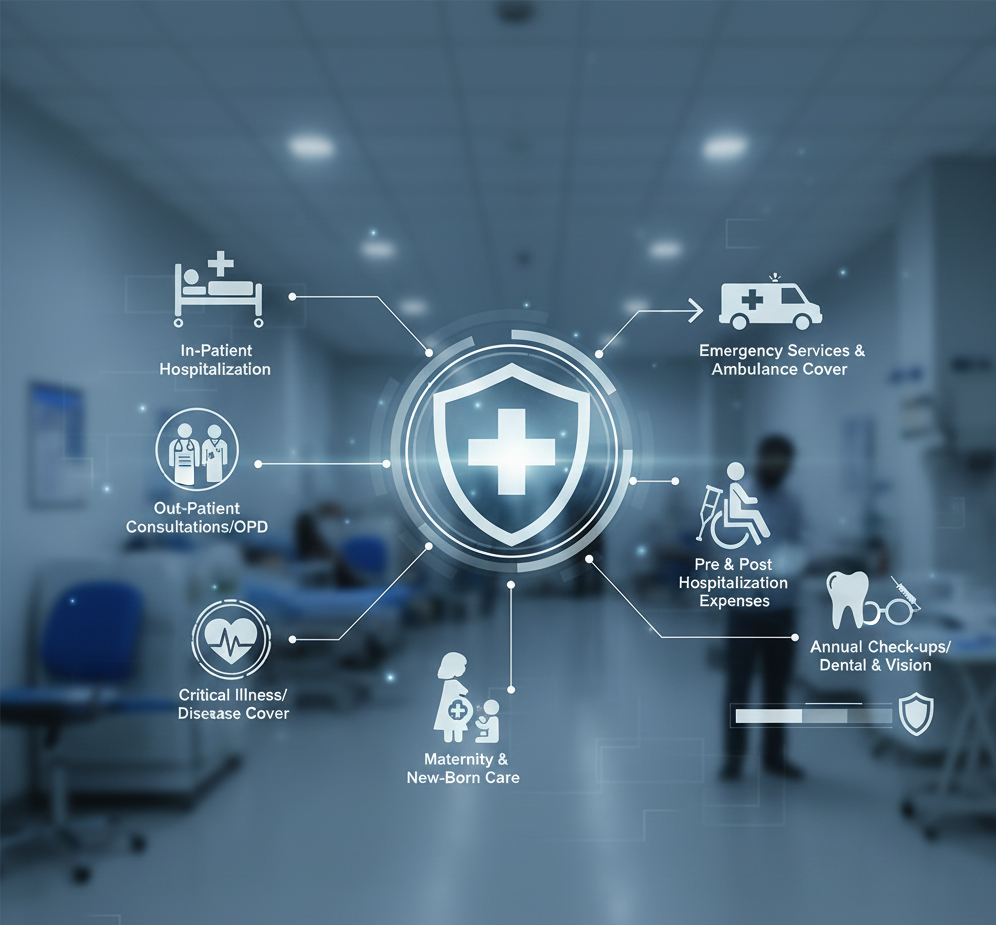

Understanding what health insurance covers prevents claim rejections and disappointment. Here’s the complete breakdown:
Standard Coverage (All Policies):
- Hospitalization: Inpatient treatment for over 24 hours including room rent, doctor fees, medicines, nursing, ICU charges
- Day-care procedures: 400+ surgeries that don’t need overnight stay (cataract, tonsillectomy, chemotherapy, dialysis)
- Pre and post-hospitalization: Medical expenses 30-60 days before admission and 60-90 days after discharge
- Ambulance charges: Up to ₹2,000-₹5,000 per hospitalization
- AYUSH treatment: Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, Homeopathy in recognized centers
Pregnancy and Maternity Coverage
Can health insurance cover pregnancy? Yes, but with conditions. Maternity coverage comes with a 9-24 month waiting period (typically 12 months). Coverage usually includes normal delivery (₹50,000-₹75,000), cesarean delivery (₹75,000-₹1.5 lakhs), pre and postnatal expenses, and newborn baby coverage for 90 days.
Not all policies include maternity. Check specifically for this benefit, as many basic plans exclude it.
Dental Coverage
Can health insurance cover dental? Partially. Dental treatment arising from accidents or hospitalizations requiring 24-hour admission is typically covered. However, routine dental work (cleaning, fillings, braces, root canal) is excluded. Some premium plans offer dental coverage as an add-on for an extra premium.
IVF and Infertility Treatment
Will health insurance cover IVF? Unfortunately, most standard policies exclude IVF, infertility treatments, and assisted reproduction. Some premium plans and international policies offer coverage with sub-limits and waiting periods. This is an expensive gap for couples seeking fertility treatment.
Pre-Existing Diseases
Will health insurance cover pre-existing conditions? Yes, after a waiting period. Pre-existing diseases are conditions you have before buying the policy – diabetes, hypertension, thyroid, asthma, etc. Standard waiting period is 2-4 years. Some insurers offer immediate coverage for extra premium.
The 2025 IRDAI guidelines encourage shorter waiting periods, and some modern plans now cover after just 1-2 years.
Modern Treatments Covered:
- LASIK eye surgery: Covered if medically necessary, not for cosmetic reasons
- Cataract surgery: Fully covered under day-care procedures
- Cancer treatment: Chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy all covered
- Organ transplants: Covered including donor expenses
- Robotic surgery: Increasingly covered under standard plans
What’s NOT Covered:
Cosmetic surgery, self-inflicted injuries, substance abuse treatment, vitamin supplements, experimental treatments, congenital diseases (varies by insurer), war and nuclear contamination, non-allopathic treatment (except AYUSH), and intentional self-harm.
Health Insurance Premiums (2025 Edition)
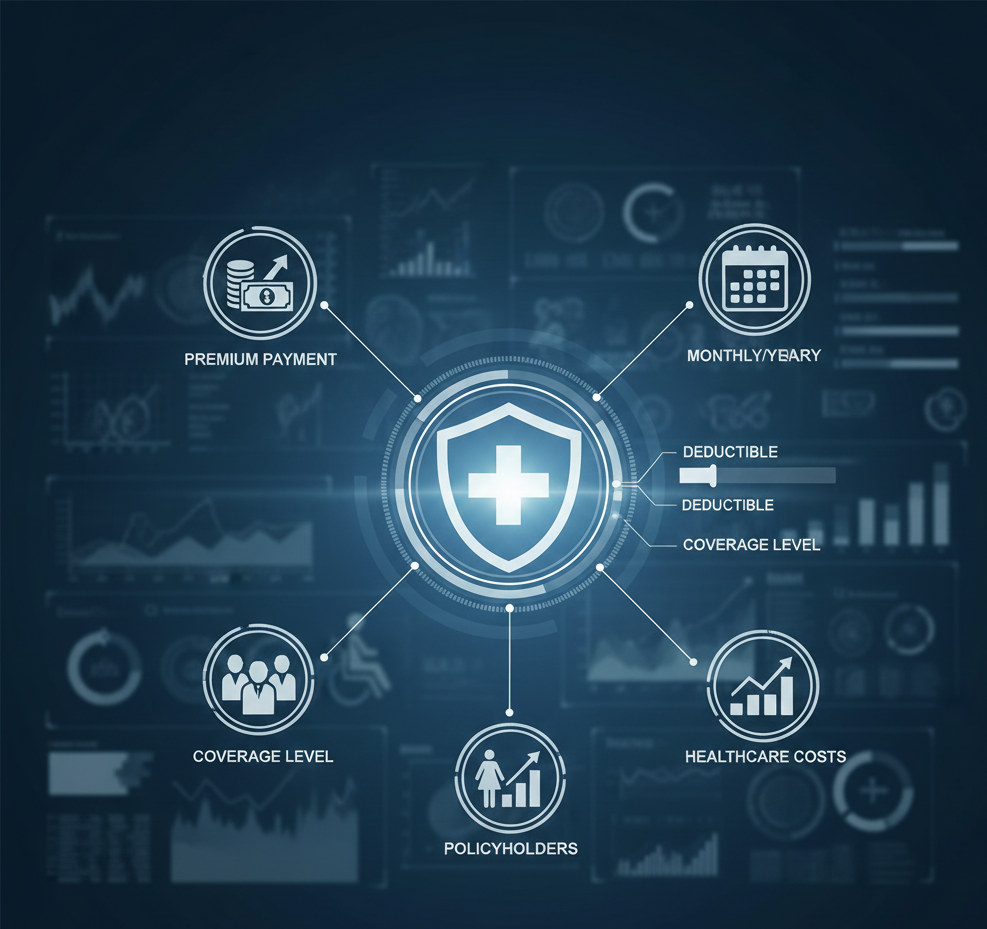

Are health insurance premiums going up? The unfortunate answer is yes. Premiums have risen 15-35% across most insurers in 2024-25, the highest jump in recent years.
Factors Affecting Your Premium:
Age: The biggest factor. A 25-year-old pays ₹6,000 for ₹5 lakh coverage, while a 45-year-old pays ₹12,000, and a 60-year-old pays ₹30,000+ for the same coverage.
Sum Insured: Higher coverage means higher premium. However, the increase is not proportional – ₹10 lakh coverage doesn’t cost double of ₹5 lakh.
Medical History: Pre-existing diseases, BMI, smoking, alcohol consumption all affect pricing. Some insurers now use AI-powered health assessments.
City: Metro residents pay 10-15% more than tier-2 city residents due to higher medical costs.
Policy Type: Family floater is cheaper per person than individual policies.
How Health Insurance Premium is Calculated:
Insurers use actuarial science and claims data. They analyze:
- Your age group’s average medical expenses
- Disease prevalence in your area
- Historical claim ratios
- Medical inflation projections
- Competitor pricing
Will health insurance premiums increase in 2025? Yes, expect another 8-15% hike. The trend will continue due to rising healthcare costs, increased disease burden, and higher claim frequencies post-COVID.
Tax Benefits on Premiums:
Are health insurance premiums tax deductible? Absolutely! Under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act:
- ₹25,000 deduction for premiums paid for self, spouse, and children
- Additional ₹25,000 for premiums paid for parents (₹50,000 if parents are senior citizens)
- Maximum combined deduction: ₹1 lakh per year
This effectively reduces your premium cost by 30% for those in the 30% tax bracket.
Monthly Payment Options:
Most insurers now offer monthly premium payment through EMI, though the total annual cost may be 3-5% higher. This improves affordability for middle-income families.
Best Health Insurance Plans in 2025 (Comparison)

Which health insurance is best in India? depends on your specific needs, but here are the top performers:
Best Overall Plans:
Niva Bupa ReAssure 2.0: Unlimited sum insured after 2 claims, no room rent limits, automatic restoration of sum insured. Premium: ₹18,000-₹22,000 for ₹10 lakh family floater.
HDFC Ergo Optima Restore: Restores sum insured if exhausted, covers 1,000+ day-care procedures, 8-year term benefits. Premium: ₹16,000-₹20,000 for ₹10 lakh family floater.
Star Health Comprehensive: Widest network of 14,000+ hospitals, excellent claim settlement ratio of 89%, strong in South India. Premium: ₹15,000-₹19,000 for ₹10 lakh family floater.
Best Family Plans:
Which health insurance is best for family? Consider:
Care Supreme: Covers all modern treatments, unlimited e-consultations, international coverage. Premium: ₹20,000-₹25,000 for family.
Manipal Cigna ProHealth Prime: Worldwide coverage, maternity from day one, mental health coverage. Premium: ₹19,000-₹24,000 for family.
Best Senior Citizen Plans:
Star Senior Citizens Red Carpet: Designed specifically for 60+ age group, covers pre-existing from year 1 with waiting period waiver option, daily hospital cash. Premium: ₹35,000-₹45,000 for ₹5 lakh.
Care Senior: Covers up to 80 years, automatic renewal for life, pre and post-hospitalization for 90 days. Premium: ₹32,000-₹42,000 for ₹5 lakh.
Regional Considerations:
Best in Kerala: KSEB & Star Health have excellent networks
Best in Tamil Nadu: Star Health, Apollo Munich dominate with extensive hospital networks
Best in Hyderabad: Care Health, Niva Bupa offer great coverage with quick cashless approvals
Top Health Insurance Companies 2025:
Based on claim settlement ratio, customer reviews, and financial strength:
- Star Health Insurance: 89% claim settlement, largest health-only insurer
- HDFC Ergo: 95% claim settlement, tech-forward processes
- Niva Bupa: 95% claim settlement, innovative products
- Care Health: 91% claim settlement, comprehensive coverage
- ICICI Lombard: 87% claim settlement, strong brand trust
How to File a Health Insurance Claim
How health insurance claim works differs between cashless and reimbursement.
Cashless Claim Process:
- Get admitted: Go to a network hospital
- Inform insurer: Hospital desk contacts insurance company (or you call within 24 hours)
- Pre-authorization: Hospital sends treatment details and estimated cost
- Approval: Insurer approves within 2-6 hours (1 hour for emergencies in 2025)
- Treatment: Receive care without payment
- Settlement: Hospital bills insurer directly
- Your payment: Only pay excluded items (room rent difference, consumables if not covered)
Reimbursement Claim Process:
- Emergency admission: Go to any hospital (network or non-network)
- Inform insurer: Call within 24-48 hours
- Pay hospital: Settle your bill and collect all documents
- Submit claim: File within 15 days with claim form, bills, discharge summary, prescriptions, diagnostic reports
- Claim assessment: Insurer reviews (usually 7-15 days)
- Settlement: Amount credited to your bank account
Required Documents:
- Duly filled claim form with hospital stamp
- Original hospital bills and receipts
- Discharge summary/certificate
- Payment receipts
- Doctor’s prescriptions
- Diagnostic test reports
- FIR copy (for accident cases)
- ID and policy proof
Why Health Insurance Claim Gets Rejected:
Top rejection reasons you must avoid:
- Incomplete documentation: Missing bills or reports (40% of rejections)
- Non-disclosure: Not informing about pre-existing conditions at policy purchase
- Waiting period: Filing claim during applicable waiting period
- Non-medical expenses: Charging items not covered (toiletries, food for attendant)
- Late intimation: Not informing insurer within specified time
- Exclusions: Claiming for explicitly excluded treatments
- Policy lapse: Premium not paid, policy inactive
- Room rent breach: Choosing room category above policy limit affects entire claim
Pro tip: Always maintain digital copies of all medical documents. Take photos of bills before submitting. Keep insurer’s claim intimation number for reference.
Renewal, Cancellation & Portability
Policy Renewal:
Can health insurance be renewed after expiry? Yes, but timing matters. Most insurers offer a grace period of 30 days after policy expiry. You can renew during this period without losing continuity benefits (waiting periods already completed).
If you miss the grace period, your policy lapses. Buying again means:
- Restarting all waiting periods
- Fresh medical underwriting
- Possible premium increase or rejection
Best practice: Set reminders 45 days before expiry. Enable auto-renewal if available.
Policy Cancellation:
Can health insurance policy be cancelled? Yes, by both parties:
You can cancel if:
- You find a better plan
- Coverage no longer needed
- Financial constraints
Refund rules: If cancelled mid-term, you get a prorated refund minus a small service charge. If no claims filed, refund is higher.
Insurer can cancel if:
- You provided false information at purchase
- Fraudulent claims filed
- Premium not paid after grace period
Portability:
Can health insurance policy be ported? Absolutely! IRDAI mandates easy portability. You can switch insurers while retaining:
- Completed waiting periods
- No-claim bonus
- Continuity benefits
Portability process:
- Apply to new insurer 45 days before current policy renewal
- New insurer requests details from old insurer
- Old insurer must respond within 7 days
- New policy starts seamlessly on renewal date
Why port: Better coverage, lower premium, better claim service, additional features, or improved network hospitals.
Important: Don’t let current policy lapse while porting. There’s no break in coverage if done correctly.
Government Health Programs (India)
Ayushman Bharat Yojana:
India’s flagship health insurance scheme covering 50 crore poor and vulnerable citizens with ₹5 lakh annual coverage per family. Treatment is completely free at empanelled hospitals.
Eligibility: Based on Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data. Rural families lacking land, living in one-room houses, having disabled members, or headed by women qualify. Urban families doing menial jobs are eligible.
Where health card apply: Visit your nearest Common Service Centre (CSC), Ayushman Mitra, or public health center. Carry Aadhaar and ration card.
Where health card renewal: Cards don’t need yearly renewal. They’re valid as long as you remain eligible under SECC criteria.
State Health Schemes:
Many states run additional programs:
- Karnataka: Suvarna Arogya Suraksha (₹3 lakh additional over Ayushman Bharat)
- Tamil Nadu: Chief Minister’s Comprehensive Health Insurance (₹5 lakh)
- Rajasthan: Bhamashah Swasthya Bima Yojana
- Maharashtra: Mahatma Jyotiba Phule Jan Arogya Yojana
Digital Health Card: Under Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, every Indian gets a unique health ID linking all medical records. Download the ABHA app to create your ID instantly.
Who health card: Any Indian citizen can create an ABHA health card free of cost. It’s not insurance but a digital health identity storing your medical history, prescriptions, and reports.
WHO Health Framework (Global Health Section)

WHO Definition of Health:
Who health definition states: “Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.” This holistic view, established in 1948, remains the global standard.
This definition revolutionized healthcare by recognizing mental health and social factors as crucial as physical health.
WHO Health System Framework:
Who health system framework comprises six building blocks:
- Service Delivery: Access to quality healthcare
- Health Workforce: Skilled doctors, nurses, and health workers
- Health Information Systems: Data collection and analysis
- Medical Products & Technologies: Medicines, vaccines, equipment
- Health Financing: Fair and sustainable funding
- Leadership & Governance: Effective health policies
India scores well on workforce and technology but struggles with equitable access and financing, especially in rural areas.
World Health Day 2025:
Who health day theme 2025 focuses on “My Health, My Right” – emphasizing universal health coverage and health equity. Observed on April 7th, it highlights the right to quality healthcare, clean water, safe environments, and discrimination-free treatment.
For India, this theme is particularly relevant as we strive to bridge the rural-urban health divide and ensure healthcare reaches every citizen regardless of economic status.
Lifestyle, Nutrition & Preventive Health
True health security combines insurance with healthy living.
Diet and Nutrition:
What health benefits of millets include high fiber, essential amino acids, low glycemic index, and rich mineral content. Millets reduce diabetes risk, improve digestion, and strengthen bones. The government’s promotion of millets as superfoods aligns with traditional Indian diets.
Are health drinks really healthy? Most commercial health drinks contain high sugar (sometimes 70% of content). They offer minimal nutritional value beyond fortified vitamins. Whole foods provide better nutrition. If you use health drinks, check sugar content and don’t rely on them as primary nutrition sources.
Are health gummies good? These trendy supplements can supplement specific deficiencies (vitamin D, B12) but shouldn’t replace balanced diets. Many contain gelatin, artificial colors, and sugars. Whole foods remain superior for most nutrients.
How Health is Affected by Lifestyle:
Physical Activity: Sedentary jobs and screen time contribute to obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. WHO recommends 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
Sleep: Indians average 6.5 hours nightly versus the recommended 7-8 hours. Poor sleep increases disease risk by 30%.
Stress: Work pressure, traffic, and financial worries create chronic stress affecting heart health and immunity.
Environment: Air pollution in Indian cities increases respiratory diseases, heart attacks, and cancer risk. Indoor air quality (cooking smoke, AC filters) also matters.
Habits: Smoking, excessive alcohol, and tobacco consumption remain major health destroyers.
Preventive Health Measures:
- Regular health check-ups: Annual blood work, ECG after 40, diabetes screening
- Vaccinations: Keep immunizations current (flu, COVID, hepatitis)
- Mental health: Practice meditation, seek counseling when needed
- Dental care: Six-monthly dental check-ups prevent serious complications
- Eye care: Annual eye exams, especially if using screens extensively
Smart tip: Many health insurance policies now include free annual health check-ups. Use this benefit proactively.
Final Recommendations for 2025
How to Choose Your Plan:
- Assess your needs: Family size, parents’ health, medical history
- Adequate sum insured: Minimum ₹10 lakh in metro cities, ₹5 lakh in smaller towns
- Check network hospitals: Ensure quality hospitals near your home are covered
- Read policy documents: Don’t rely only on brochures
- Claim settlement ratio: Choose insurers with 85%+ settlement ratio
- Customer reviews: Check actual claim experiences online
- Waiting periods: Shorter is better, especially for pre-existing conditions
- Additional features: Look for restoration, no-claim bonus, unlimited renewals
What to Avoid:
- Buying only based on price: Cheapest isn’t always best
- Insufficient coverage: Medical inflation makes ₹2-3 lakh inadequate
- Ignoring exclusions: Read what’s NOT covered carefully
- Not disclosing medical history: This causes claim rejections
- Letting policy lapse: Restart waiting periods from scratch
- Relying solely on corporate cover: Always have personal backup
Predictions for 2025-2030:
Technology integration: AI-driven instant claim approvals, blockchain-based health records, telemedicine as standard coverage.
Personalized pricing: Wearable device data influencing premiums – healthier lifestyles earning discounts.
Comprehensive mental health: Full coverage for therapy, counseling, and psychiatric treatment.
Wellness focus: Insurers rewarding preventive health activities with premium discounts and cashbacks.
Regulatory improvements: Faster claim settlements, standardized policy terms, mandatory coverage for advanced treatments.
Medical inflation: Expect healthcare costs to rise 12-15% annually, making adequate coverage more critical.
Best Health Practices:
Combine insurance with prevention. No policy can replace healthy living. Exercise regularly, eat balanced diets, manage stress, get adequate sleep, and undergo annual health screenings.
Your health insurance strategy: Buy young when premiums are low, opt for adequate coverage (minimum ₹10 lakh), add top-up plans for extra protection, review coverage annually as family needs change, and maintain policy continuity without breaks.
Final thought: Health insurance in India 2025 isn’t optional – it’s essential. With rising medical costs and unpredictable health challenges, adequate coverage protects your family’s financial future while ensuring access to quality healthcare when needed most.
Ready to secure your family’s health? Compare plans from top insurers, read policy documents carefully, and invest in comprehensive coverage today. Your future self will thank you.

