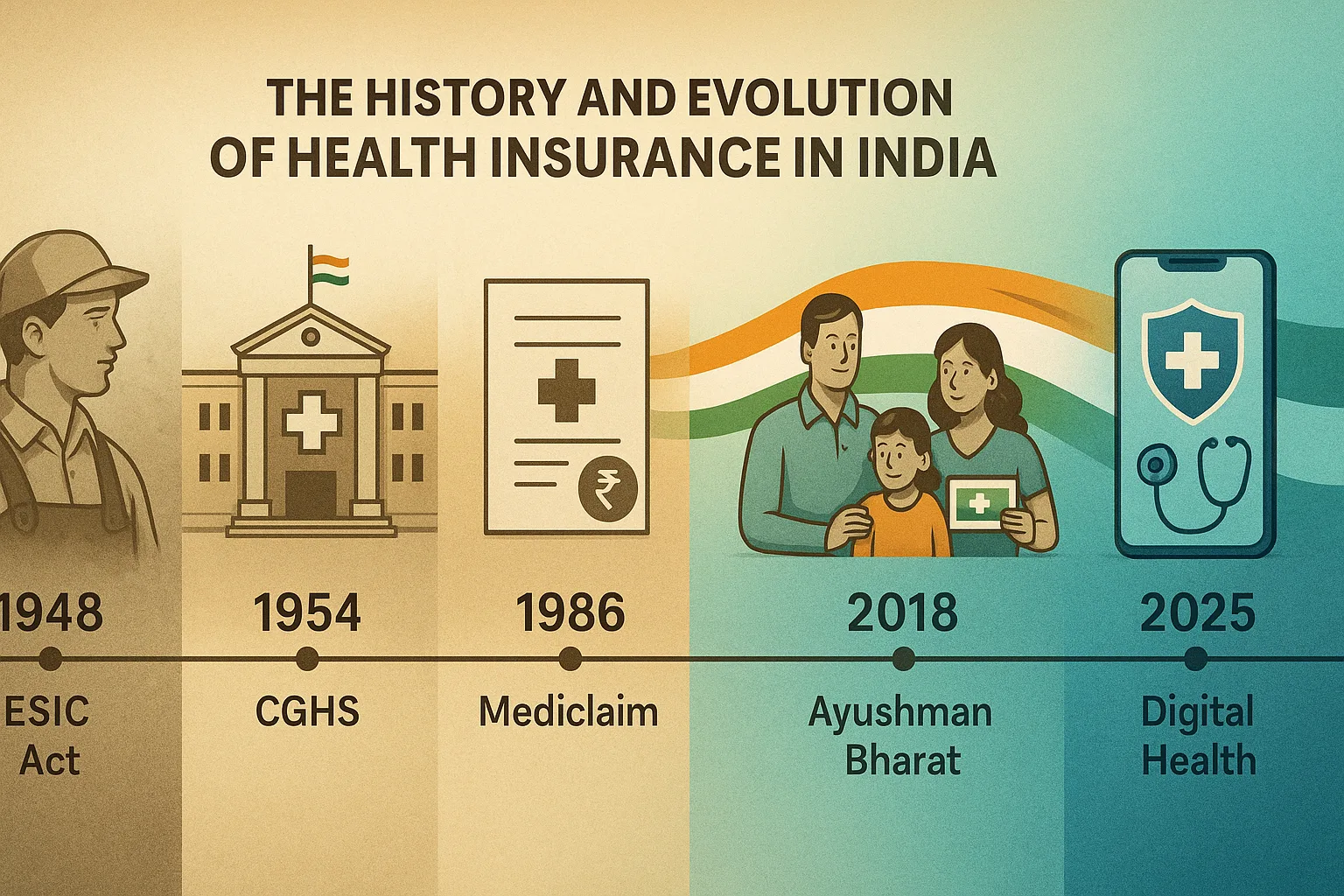
From Government Schemes to Digital Revolution
The story of health insurance in India spans over 75 remarkable years—from basic employee coverage in 1948 to today’s AI-powered instant cashless claims. Understanding when health insurance started in India helps us appreciate how far we’ve come and where we’re headed.
In 1948, newly independent India took its first bold step toward healthcare protection. Fast forward to 2025, and over 50 crore Indians now have health insurance—a transformation that mirrors the nation’s own journey from socialist schemes to digital innovation.
This isn’t just a timeline of policies. It’s the story of how India built one of the world’s fastest-growing health insurance markets, learning from global models while adapting to local needs.
The Foundation Years: 1940s–1980s
1948: The Birth – ESIC Act
When health insurance started in India dates to November 19, 1948, when the Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) Act was passed—barely 15 months after independence.
The Vision:
Labor Minister Jagjivan Ram, inspired by Britain’s social security model, created comprehensive healthcare for factory workers who couldn’t afford medical treatment on meager wages.
How ESIC Worked:
- Coverage: Factory workers earning below ₹3,000/month
- Contribution: Employees paid 1.75%, employers paid 4.75% of wages
- Benefits: Free treatment at ESI hospitals, maternity benefits, disability coverage
- First Hospital: Opened in Kanpur in February 1952
Impact: By 1960, 1.5 million workers were covered. By 1980, this grew to 18 million. Today, ESIC covers over 13 crore beneficiaries with 1,500+ hospitals—the largest employer-based health scheme in Asia.
1954: Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS)
While ESIC protected factory workers, government employees needed coverage too. On April 4, 1954, CGHS launched in Delhi.
The Structure:
- Eligibility: Central government employees and pensioners
- Contribution: ₹15-50 monthly based on pay scale
- Coverage: OPD consultations, hospitalization, medicines at empanelled facilities
Historical Importance: CGHS introduced the cashless treatment model decades before private insurers. Employees showed their card at hospitals and received treatment without payment—hospitals billed CGHS directly. This became the template for modern cashless insurance.
Growth: Started with 100,000 beneficiaries in Delhi, CGHS now covers 40+ lakh families across 73+ cities.
1986: Mediclaim – The First Public Health Insurance
The true beginning of consumer health insurance came on November 1, 1986, when four public sector insurers launched Mediclaim Policy—India’s first standalone health insurance product.
What Mediclaim Offered:
- Sum Insured: ₹15,000 to ₹5 lakhs
- Coverage: Hospitalization, surgery, room rent, ICU
- Premium: ₹500-5,000 annually
- Innovation: Covered pre-existing diseases after 4 years
Why It Struggled Initially:
In 1986, hospitalization was rare, treatment costs low (₹5,000-10,000 for major surgery), and joint families provided financial support. Premium of ₹1,000 seemed expensive. By 1990, only 2-3 lakh policies sold nationwide.
Legacy: Despite slow adoption, Mediclaim established crucial concepts—individual health coverage, voluntary purchase, and premium-based protection—laying groundwork for the revolution ahead.
The Expansion Era: 1990–2005
1991: Economic Liberalization
Economic reforms of 1991 transformed everything:
- Private hospitals emerged (Apollo, Fortis, Max)
- Healthcare costs rose 8-10% annually
- Middle class expanded from 3 crore to 8 crore households
- Medical technology advanced—MRI, CT scans became standard
- Health awareness increased
Suddenly, Mediclaim made sense. By 1995, sales grew to 15 lakh policies.
2000: IRDA Opens the Market
The most transformative moment came on April 19, 2000, when the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) opened India’s insurance market to private players after 47 years of public sector monopoly.
First Private Entrants (2001-2003):
- ICICI Lombard (2001): Brought bancassurance model
- Bajaj Allianz (2001): Introduced international practices
- HDFC Ergo (2002): Focused on customer service
- Max Bupa (2006): Specialized pure health insurance
What Changed:
- Competition: Premium rates became competitive
- Innovation: Family floater plans, critical illness riders, hospital cash
- Service: Faster claim processing, toll-free helplines
- Distribution: Online sales, bank partnerships, comparison websites
- Products: Tailored plans for seniors, women, specific diseases
Growth Explosion:
From 30 lakh policies (2000) to 2.5 crore policies (2010)—over 8x growth in a decade.
2001: Third Party Administrators (TPAs)
IRDA allowed TPAs—intermediaries managing cashless claims between insurers and hospitals. This revolutionized claim processing.
How TPAs Work:
- Hospital sends treatment details to TPA
- TPA verifies policy coverage
- TPA approves/rejects cashless authorization
- Hospital bills TPA, TPA settles with insurer
Impact: Cashless network expanded from 500 hospitals (2001) to 5,000+ hospitals (2010). Claim processing reduced from 45 days to 15 days.
2003-2005: Product Innovation Begins
2003 – Critical Illness Plans: Lump sum payment on diagnosis of cancer, heart attack, kidney failure.
2004 – Senior Citizen Plans: Specialized coverage for 60+ age group with higher premiums but pre-existing disease coverage.
2005 – Family Floater Plans: One policy covering entire family with shared sum insured—reducing premium by 30-40% vs individual policies.
Modernization Era: 2005–2020
2013: IRDAI (Health Insurance) Regulations
IRDAI introduced comprehensive health insurance regulations bringing standardization and consumer protection.
Key Reforms:
- Standardized Terms: Clear definitions of “hospitalization,” “pre-existing disease,” “emergency”
- Portability Rights: Switch insurers without losing accrued benefits
- Grace Periods: 30 days to renew without losing coverage
- Grievance Redressal: Insurance Ombudsman for complaint resolution
- Mandatory Coverage: Mental health, modern treatments must be covered
2018: Ayushman Bharat – The Game Changer
On September 23, 2018, Prime Minister Modi launched Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY)—the world’s largest government-funded health insurance program.
The Vision:
Universal health coverage for 50 crore poor and vulnerable Indians—the bottom 40% of population.
Coverage Details:
- Sum Insured: ₹5 lakhs per family per year
- Beneficiaries: 10.74 crore families = 50+ crore individuals
- Coverage: 1,949 treatment packages including surgeries, therapies, diagnostics
- Cost to Beneficiary: Completely free
- Empanelled Hospitals: 27,000+ (2025)
Impact (2018-2025):
- 7.3 crore hospital admissions
- ₹91,000+ crores claimed
- Reduced out-of-pocket healthcare expenses by 48% for beneficiaries
- Expanded insurance awareness to rural India
Significance: Ayushman Bharat brought health insurance into national consciousness. Families who never heard of insurance now understand cashless treatment, empanelled hospitals, and coverage limits.
2017-2020: Specialized Products Boom
2017 – Maternity Add-Ons: Coverage for pregnancy, delivery, newborn care with waiting periods.
2018 – OPD Plans: Outpatient consultation coverage—doctor visits without hospitalization.
2019 – Top-Up/Super Top-Up Plans: Affordable high-value coverage with deductibles.
2020 – Corona Kavach: Pandemic-specific policies mandated by IRDAI during COVID-19.
Digital Transformation: 2020–2025
The COVID-19 Catalyst
The pandemic accelerated digital adoption by 5-10 years almost overnight.
March 2020 – Crisis Hits:
- Claim volumes surged 300%
- Physical branch visits impossible during lockdown
- Paper-based processes collapsed
- Need for instant approvals became critical
Industry Response:
- Online Policy Purchase: Jumped from 30% to 75% of all sales
- Digital Claims: Mobile app submissions became standard
- Video KYC: Remote policy issuance without physical verification
- Telemedicine Coverage: Virtual doctor consultations covered
- AI Claim Processing: Automated approvals for straightforward claims
2021-2025: Technology Revolution
Digital Health Cards
What Changed:
Physical insurance cards replaced by digital e-cards stored on mobile apps. QR code scanning at hospitals instantly verifies coverage.
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (2021): Every Indian gets unique Health ID linking all medical records, prescriptions, insurance policies. Over 50 crore Health IDs created by 2025.
Instant Claim Approvals
2025 IRDAI Mandate: Cashless claims must be approved within 1 hour for genuine emergencies. AI-powered systems analyze claims in minutes.
How It Works:
- Hospital uploads patient details and treatment plan
- AI verifies policy status, coverage, medical necessity
- Approval in 15-30 minutes for standard procedures
- Complex cases routed to medical experts—decision in 2-4 hours
Impact: 85% of cashless claims now approved within 1 hour vs 6-12 hours in 2020.
Mobile-First Experience
Today’s Journey:
- Research plans on comparison websites
- Buy policy entirely on smartphone in 10 minutes
- Upload documents via app
- Track claim status real-time
- Renew with one click
- Port to new insurer digitally
Statistics (2025):
- 78% policies purchased online (vs 32% in 2019)
- 92% claims filed digitally
- 4.5+ crore health insurance app users
Telemedicine Integration
Pandemic Legacy: Virtual doctor consultations now covered by all major insurers. Free telemedicine included with policies.
Usage: 12+ crore telemedicine consultations covered by insurance in 2024, reducing unnecessary hospital visits.
2023-2025: IRDAI’s Consumer-Friendly Reforms
2023 – “Insurance For All by 2047” Vision:
IRDAI Chairman Debasish Panda announced ambitious goal—universal insurance coverage by India’s 100th independence year.
Key 2024-2025 Reforms:
1. No Room Rent Caps (2024):
Insurers eliminating room rent restrictions. Earlier, policies limited room rent to 1-2% of sum insured, creating co-payment issues. New policies offer unlimited room rent.
2. Mental Health Parity:
Psychiatric treatment, counseling, therapy now covered at par with physical illness.
3. Reduced Waiting Periods:
Pre-existing disease waiting periods reduced from 4 years to 2-3 years for most conditions.
4. OPD Inclusion:
Encouraging bundled policies including outpatient consultations, not just hospitalization.
5. Use & File Products:
Insurers can launch products immediately without waiting for IRDAI approval—faster innovation.
6. Standardized Exclusions:
IRDAI working on uniform exclusion list so consumers can compare policies easily.
The Present: Where We Stand in 2025
Market Size & Penetration
Statistics (2025):
- Total Insured: 52 crore Indians (38% of population)
- Ayushman Bharat: 50 crore
- Private Health Insurance: 14 crore
- ESIC/CGHS: 15 crore
- (Some overlap exists)
- Premium Collection: ₹95,000+ crores annually
- Number of Insurers: 34 companies offering health insurance
- Claim Settlement Ratio: Industry average 88%
- Network Hospitals: 27,000+ (Ayushman Bharat) + 14,000+ (private insurers)
What’s Available Today
Product Diversity:
- Individual, family floater, senior citizen plans
- Critical illness, cancer-specific policies
- Top-up, super top-up plans
- International coverage options
- Short-term, long-term options
- OPD, dental, vision add-ons
- Wellness benefits, health check-ups
- Mental health coverage
Sum Insured Options: ₹1 lakh to ₹2 crores—something for every budget.
Premium Range: ₹3,000 to ₹1,50,000+ annually based on age, coverage, add-ons.
The Future: 2025–2030
Emerging Trends
1. Personalized Pricing:
Wearable devices (Fitbit, Apple Watch) tracking health metrics. Healthier individuals get premium discounts up to 25%. Already piloted by Niva Bupa, Max Bupa.
2. Blockchain Claims:
Immutable records preventing fraud. Pilot projects by HDFC Ergo show 40% faster claim processing.
3. Preventive Care Focus:
Insurers offering free gym memberships, nutrition counseling, health coaching—keeping policyholders healthy reduces claims.
4. AI Underwriting:
Instant policy issuance based on AI health risk assessment—no medical tests required up to 50 years.
5. Lifetime Renewability:
Guaranteed renewal for life regardless of claim history—already offered by leading insurers.
6. Wellness Ecosystems:
Integration with pharmacy apps (Netmeds, PharmEasy), diagnostic labs (Thyrocare, Dr. Lal PathLabs), fitness apps (HealthifyMe)—one app managing entire health journey.
IRDAI’s Vision for 2030
Goals Announced:
- 80% Population Coverage: From current 38% to 80% by 2030
- Cashless Everywhere: Every hospital must offer cashless claims
- 1-Hour Approvals: For all claims, not just emergencies
- No Claim Rejections: Unless fraud—benefit of doubt to policyholder
- Micro-Insurance: Plans for ₹1-2 lakh coverage at ₹500-1,000 premium for low-income families
- Rural Penetration: Mobile insurance vans, vernacular apps, simplified products
Conclusion: A Journey of Transformation
The history of health insurance in India is a testament to progress. From ESIC’s modest beginning covering 1.5 lakh workers in 1952 to 52 crore Indians covered today, we’ve come extraordinarily far.
Key Milestones:
- 1948: ESIC creates foundation
- 1986: Mediclaim introduces individual coverage
- 2000: Private insurers enter, competition begins
- 2018: Ayushman Bharat achieves mass coverage
- 2025: Digital-first, instant cashless approvals
What Remains:
Despite progress, 62% of Indians still lack health insurance. Out-of-pocket medical expenses push 5.5 crore Indians into poverty annually. The journey continues.
The Promise Ahead:
With technology, regulatory support, increasing awareness, and innovative products, India is poised to achieve universal health coverage by 2047—ensuring every citizen can access quality healthcare without financial devastation.
Related Resources:
- How Health Insurance Works in India – Understanding the basics
- Best Health Insurance Plans 2025 – Compare top insurers and coverage
- Health Insurance Premiums Guide – Why costs are rising and how to save
- Complete Coverage Guide – What’s covered and excluded
- Health Cards & Government Schemes – Ayushman Bharat and CGHS details
The story of health insurance evolution in India continues to unfold. As consumers, understanding this history helps us appreciate current protections and advocate for future improvements. From paper forms to digital health IDs, from 30-day claim processing to 1-hour approvals—we’re living in the golden age of health insurance accessibility. The best is yet to come.